#76
Intro to Trampoline
| Difficulty: | Medium |
| Topics: | recursion |
The trampoline function takes a function f
and a variable number of parameters.
Trampoline calls f with any parameters that were supplied.
If f returns a function, trampoline
calls that function with no arguments.
This is repeated, until the return value is not a function,
and then trampoline returns that non-function value.
This is useful for implementing mutually recursive algorithms
in a way that won't consume the stack.
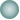 | (= __
(letfn
[(foo [x y] #(bar (conj x y) y))
(bar [x y] (if (> (last x) 10)
x
#(foo x (+ 2 y))))]
(trampoline foo [] 1))) |
